The low-cut filter reduces or eliminates low-frequency sounds below a certain threshold. It’s sometimes referred to as a high-pass filter, since it allows higher frequencies to pass through while cutting out the lower ones. By attenuating low frequencies, a low-cut filter can help remove rumble, handling noise, wind noise, or other unwanted low-frequency content that may muddy a mix or cause distortion.
The cut-off frequency in a low-cut filter is the frequency at which the filter begins to significantly reduce the amplitude of frequencies below that point. This frequency isn’t a strict “on/off” boundary; instead, it marks the start of a gradual attenuation. For example, if the cut-off frequency is set at 80 Hz, the filter will start rolling off frequencies below 80 Hz. The slope of this attenuation (filter order) determines how quickly the low frequencies diminish as they get further from the cut-off point.
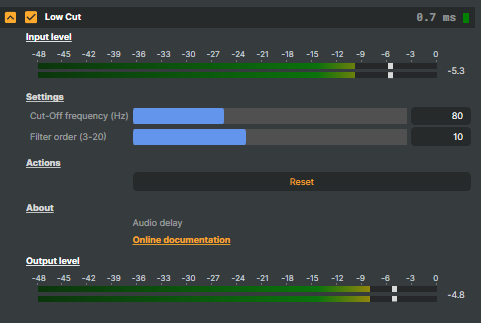
This operator displays the audio input level before processing and the output level after the operator has been applied, allowing you to monitor how the adjustments affect the signal.
A miniature audio meter (VU meter) in the header indicates incoming audio, so you can quickly verify that the operator is receiving audio even when it is collapsed.
Use Settings to adjust how long the signal overload indicator stays active, and Project Options to change the maximum peak level displayed in all audio meters to your preference.
Settings
- Cut-off frequency (Hz) - The frequency at which the filter begins to significantly reduce the amplitude of frequencies below that point
- Filter order (3-20) - Determines how quickly the low frequencies diminish as they get further from the cut-off point.
For more information on audio, see Working with audio in scenes.
(The operator is available in Composer R1 2025 and later releases)