Trackers/Histogram
The Histogram Operator is a powerful real-time tool for analyzing video content based on content colors (hue, saturation and value, or HSV in short).
The core of the operator has one major function: count the number of instances of each unique color. This calculation can also be described as a HSV-histogram: A histogram is a mathematical representation of how common a certain value is. In this case, the histograms keeps track of the most common color = hue, saturation and value (HSV).
The operator is very flexible and can be used in many different ways and in many use-cases. This flexibility comes with a bit of a drawback: complexity. This operator is one of the most complex operators to describe and to understand.
The best way of thinking of this operator is as if it were a "filter": you define an HSV selection and additional criteria, and if those are fulfilled the operator will consider your content (video frame) to be qualified. If your criterias also include a Temporal filter (content over time), the operator will analyze the content over a number of frames and provide additional options for the content to be qualified.
The video analysis engine of the operator can be restricted to a certain part of the video (Processing Area).

The configuration below will detect a green area and show the qualified pixels as pink (To see the qualified pink pixels, uncheck the “Video pass-through” checkbox). Unchecking the “Show qualified pixels” will still detect the green pixels but not visually show them as pink.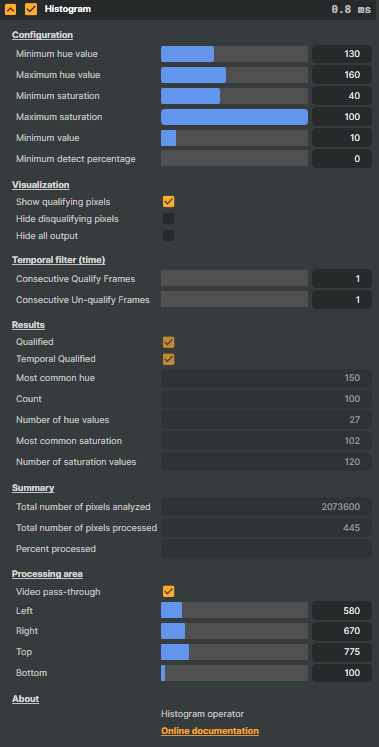
Configuration
In this section, you define the criteria, or "filters", for qualifying pixels.Minimum hue value - the minimum hue (0-360)
Maximum hue value - the maximum hue (0-360)
Minimum saturation - the minimum saturation (0-100 %)
Maximin saturation - the maximum saturation (0-100 %)
Maximum value - the maximum value (0 - 100%)
Minimum detection percentage - defines the minimum percentage of pixels that needs to qualify.
Visualization
Show qualifying pixels - when selected, all qualifying pixels will be shown as pink pixels.
Hide disqualifying pixels - when selected, all pixels that don’t qualify will be hidden.
Hide all output - hides all pixels that are being processed.
Temporal filter (time)
Consecutive Qualify Frames - the number of consequent frames that needs to qualify for the Temporal Qualified check to pass (become true).
Consecutive Un-qualify Frames - the number of consequent frames that needs to be disqualified for the Temporal Qualified check to pass (become true).
Results
Qualified - true/checked if the frame qualified.
Temporal Qualified - true/checked if the frame is qualified using the temporal filter.
Most common hue - the most common hue in the frame
Count - the number of pixels having the most common hue
Number of hue values - the number of unique hue values
Most common saturation - the most common saturation in the frame
Number of saturation values - the number of unique saturation values
Summary
Total number of pixels analyzed
Total number of pixels processed
Percent processed
Processing area
Video-pass-through - when selected, the operator will not make any visual changes to the image.
Left - crop left
Right - crop right
Top - crop top
Bottom - crop bottom
Tutorial
One example on how to use the Histogram operator can be found in the Roulette Replay tutorial.